The Spectrum of Rabbit Fur Colors
Introduction: Rabbit fur, with its variety of textures and a wide spectrum of colors, is as diverse as it is beautiful. From the deep, rich blacks to the purest whites and everything in between, the world of rabbit fur colors is a fascinating subject for breeders, pet owners, and rabbit enthusiasts alike. This blog delves into the genetics behind rabbit fur colors, shares insights on how to breed for specific shades, and highlights some exemplary cases of unique and stunning fur colors in rabbits.
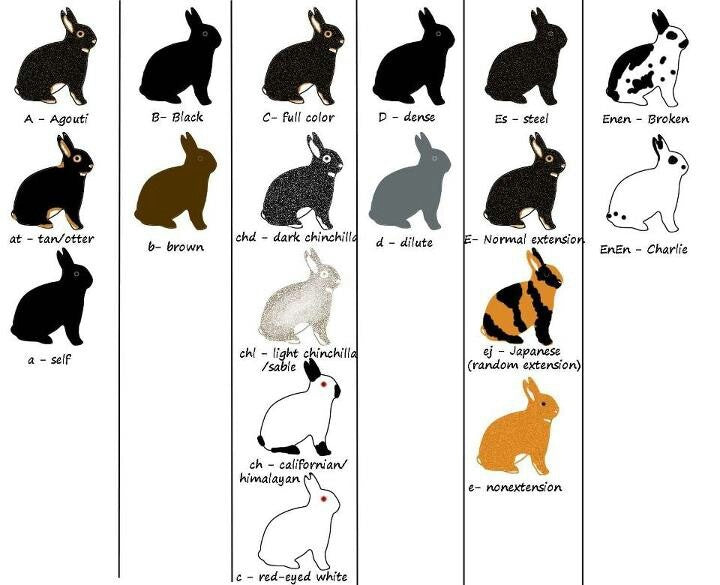
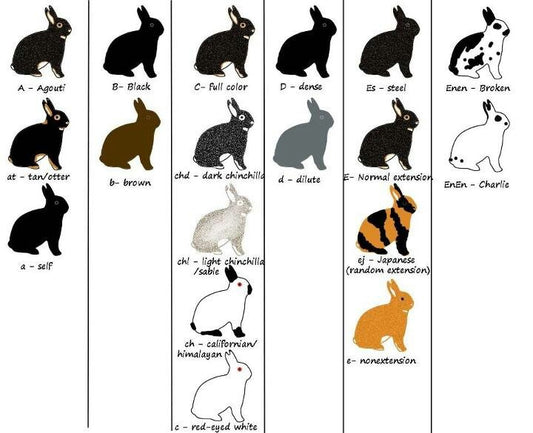
Understanding Rabbit Fur Color Genetics
The color of a rabbit's fur is determined by a combination of genetic factors, with several genes involved in dictating the final hue. The primary gene responsible for fur color is the agouti gene, which controls whether the fur is a solid color (non-agouti) or has a banded pattern (agouti). Other genes influence the intensity of the color, shading, and whether the color is dilute or rich.
Common Fur Colors and Patterns
Rabbits come in a wide array of colors and patterns, ranging from single, solid colors to complex patterns involving multiple shades. Some of the most common fur colors include:
- Black: A solid, deep black throughout the entire fur.
- White: Pure white fur can be the result of either the albino gene or the REW (Red-Eyed White) gene.
- Blue: A dilute version of black, resulting in a beautiful, soft blue-gray color.
- Chocolate: A rich, deep brown color, which is a dilution of the black gene.
- Agouti: The natural rabbit color, with banded fur in shades of brown, gray, and black, mimicking the appearance of wild rabbits.
Breeding for Color
Breeding rabbits for specific fur colors requires a thorough understanding of rabbit genetics and careful selection of breeding pairs. For example, breeding two REW rabbits will always produce white offspring, while breeding a black rabbit with a blue one might result in a litter with both colors, depending on their genetic makeup.
Case Studies: Unique Rabbit Colors
-
1. Harlequin Rabbits: The Artistic Splendor
Harlequin rabbits are a striking example of rabbit color diversity, characterized by their alternating bands of color and white. This pattern resembles a patchwork or mosaic, giving them an almost painted appearance. The Harlequin pattern is not a result of selective color breeding but rather a specific gene that segments color distribution. Originating from France, this breed was initially developed in the 1880s and has since been a show favorite. Breeding Harlequin rabbits requires a deep understanding of color genetics, as the desired outcome is to achieve a perfect balance between the base color and its contrasting patches.

2. The Opal Rabbit: A Glimmering Gem
The Opal rabbit showcases a mesmerizing blue-gray coat with warm, underlying brown tones, making it one of the most beautiful and sought-after rabbit fur colors. This color results from a unique combination of the chocolate color gene diluted by a non-extension gene, along with the agouti gene that adds the banded pattern of light and dark across each strand of fur. The effect is a coat that gleams and shifts in different lights, much like its namesake gemstone. The Opal color is most commonly seen in breeds like the Mini Rex, where the plush, velvety texture of the Rex fur further enhances the color's depth and appeal.

3. The Siamese Sable: The Mysterious Shadow
Siamese Sable rabbits exhibit a rich, sepia-toned color that darkens towards the extremities, creating a striking contrast and an almost ethereal appearance. This color is controlled by a series of genes responsible for shading, which gradually darkens the fur from a lighter body color to darker points on the ears, face, tail, and feet. The depth and intensity of the color can vary significantly, from light to deep sable, depending on the genetic makeup and the presence of modifying genes. Breeding for this particular shade requires a precise selection of parents to achieve the desired gradient effect.

4. Blue of Sint-Niklaas: A Rare Belgian Beauty
The Blue of Sint-Niklaas is a rare and historically significant rabbit breed, known for its uniform, deep blue color. Originating from Belgium, this breed's color is the result of a dilution gene acting on black fur, creating a solid, even blue hue throughout. The breed is named after the town of Sint-Niklaas, where it was first developed, and has become a symbol of Belgian rabbit breeding excellence. The Blue of Sint-Niklaas is not only prized for its color but also for its role in the development of other blue rabbit breeds across Europe.

Caring for Colored Fur
Regardless of color, rabbit fur requires regular grooming to keep it in good condition. Long-haired breeds like the Angora require daily brushing to prevent mats and tangles, while even short-haired breeds benefit from regular grooming to remove loose fur and prevent hairballs.
Conclusion
The diversity of rabbit fur colors is a testament to the complex genetics at play and the careful breeding practices of rabbit enthusiasts around the world. Whether you're a breeder aiming to produce a specific color or a pet owner who's simply curious about the science behind your furry friend's coat, the world of rabbit fur colors is endlessly intriguing. By understanding the basics of genetics and providing proper care, you can appreciate the beauty of rabbit fur in all its shades and patterns.
To ensure your rabbits have a safe and comfortable environment, consider investing in a ZiDtia chicken coop. Not only is it affordable, but its spacious design makes it perfect for DIY modifications to suit your specific needs. Whether you want to create a custom living space for your rabbits or add extra features to enhance their comfort, the ZiDtia chicken coop offers the flexibility and size to accommodate your creative ideas. Check out the ZiDtia chicken coop today and give your rabbits the home they deserve!
No comments

















0 comments